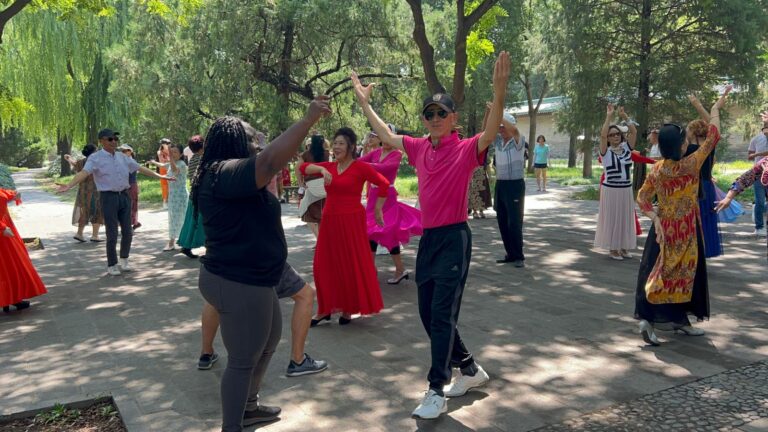Health Archives - Barbados Today
WHO authorises second vaccine against dengue amid outbreaks in the Americas
The World Health Organization on Wednesday authorised a second dengue vaccine, a move that could provide protection for millions worldwide against the mosquito-borne disease that has already sparked numerous outbreaks across the Americas this year.
In a statement on Wednesday, the UN health agency said it approved the dengue vaccine made by the Japanese pharmaceutical Takeda, recommending its use in children between six to 16 years old living in regions with high rates of dengue. The two-dose vaccine protects against the four types of dengue.
Takeda’s dengue vaccine, known as Qdenga, was previously given the nod by the European Medicines Agency in 2022.
WHO’s approval now means that donors and other UN agencies can purchase the vaccine for poorer countries.
Studies have shown Takeda’s vaccine is about 84% effective in preventing people from being hospitalised with dengue and about 61% effective in stopping symptoms.
WHO’s Rogerio Gaspar, director for the agency’s approvals of medicines and vaccines, said it was “an important step in the expansion of global access to dengue vaccines.” He noted it was the second immunisation the UN agency had authorised for dengue.
The first vaccine WHO approved was made by Sanofi Pasteur, which was later found to increase the risk of severe dengue in people who had not previously been infected with the disease.
There is no specific treatment for dengue, a leading cause of serious illness and death in roughly 120 Latin American and Asian countries. While about 80% of infections are mild, severe cases of dengue can lead to internal bleeding, organ failure and death.
Last week WHO reported there were 6.7 million suspected cases of dengue in the Americas, an increase of 206% compared with the same period in 2023. In March, authorities in Rio de Janeiro declared a public health emergency over its dengue epidemic and the country began rolling out the Takeda vaccine, aiming to inoculate at least three million people.
Last year WHO said cases of dengue have spiked tenfold over the last generation, with climate change and the increasing range of the mosquitoes that carry dengue partly to blame for the disease’s spread.
SOURCE: AP
The post WHO authorises second vaccine against dengue amid outbreaks in the Americas appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 2 months ago
Health, World
As cholera cases rise worldwide, health officials sound 'concerning' alarm about vaccine shortages
As cholera continues to surge — and as vaccines remain in short supply — experts are warning about the global risk.
Cholera is a bacterial disease typically spread by food and water, leading to severe diarrhea and dehydration. It has been on the rise around the world since 2021.
As cholera continues to surge — and as vaccines remain in short supply — experts are warning about the global risk.
Cholera is a bacterial disease typically spread by food and water, leading to severe diarrhea and dehydration. It has been on the rise around the world since 2021.
Each year, there are some 1.3 to 4 million cases of cholera worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Approximately 21,000 to 143,000 deaths occur as a result.
HIGH LEVELS OF RESISTANT BACTERIA FOUND IN UNCOOKED MEATS AND RAW DOG FOOD: ‘RED FLAG’
Around 473,000 cases were reported to WHO in 2022, which was twice as many cases as the prior year.
Reported cases for 2023 are expected to exceed 700,000.
"It is concerning to see an increase in the number of cholera cases worldwide, with the majority of the cases in Asia, Africa and Latin America," Dr. Renuga Vivekanandan, M.D., assistant dean and professor at the Creighton University School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska, told Fox News Digital.
The countries most affected include the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Haiti, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Zambia and Zimbabwe, according to UNICEF.
Although cholera cases were prevalent in the U.S. in the 1800s, water treatment systems have largely eliminated the disease, per the CDC.
In rare cases, people in the U.S. have contracted the disease from consuming raw or undercooked shellfish from the Gulf of Mexico, the agency stated on its website.
AMID BIRD FLU SPREAD, EXPERTS REVEAL IF IT'S SAFE TO DRINK MILK: 'INDIRECT CONCERN'
"In the U.S., the cases have remained very small and are usually from travel exposure," Vivekanandan noted.
Cholera is typically spread when someone drinks water or eats food that is contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, according to the CDC.
The disease can spread quickly in locations where there is insufficient treatment of drinking water and sewage, the agency warned.
It is not typically transmitted from person to person.
UNICEF noted in a statement that the rise in cholera is driven by "persistent gaps in access to safe water and sanitation."
"I think the cases might be increasing due to climate change, displacements of homes due to disasters, and not having good sanitary conditions, such as poor water sources," Vivekanandan told Fox News Digital.
Around 10% of the people who are infected with cholera will develop severe symptoms, including watery diarrhea, vomiting and leg cramps, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Advanced symptoms include shock and dehydration.
Without treatment, the disease can be fatal.
"Dehydration is the biggest concern with cholera, and rehydration is the most important component of treatment," said Vivekanandan.
"Most patients with cholera will have mild diarrhea, but 10% will have severe diarrhea and will need rehydration and treatment with antibiotics."
WITH WHOOPING COUGH CASES ON THE RISE, DO YOU NEED A BOOSTER VACCINE?
Some groups are more susceptible to the disease, according to the CDC.
"Individuals with achlorhydria (the absence of hydrochloric acid in digestive stomach juices), blood type O, chronic medical conditions, and those without ready access to rehydration therapy and medical services are more likely to have severe disease from cholera and suffer poor outcomes," the agency noted.
The most effective treatment for cholera is "immediate replacement of the fluid and salts lost through diarrhea," the CDC stated.
This is achieved by giving patients a mixture of sugar and salts mixed with 1 liter of water.
In some severe cases, the patient may require intravenous (IV) fluids.
Some patients also receive antibiotics to make symptoms less severe.
"Persons who develop severe diarrhea and vomiting in countries where cholera occurs should seek medical attention promptly," per the CDC.
There is a single-dose vaccine for cholera, called Vaxchora (lyophilized CVD 103-HgR).
CDC WARNS OF INVASIVE BACTERIAL OUTBREAK AMID SPIKE IN CASES AND FATALITY RATES: 'RARE BUT SEVERE'
Those who are between the ages of 2 and 64 and who are traveling to "an area of active cholera transmission" are eligible to receive it.
There are three other cholera vaccines, but they are not available in the U.S.
There is a "severe gap" in the number of available vaccine doses compared to the level of current need, said UNICEF on its website.
"Between 2021 and 2023, more doses were requested for outbreak response than the entire previous decade," UNICEF noted.
While cholera vaccines used to be administered in two doses, the International Coordinating Group (ICG) changed the recommendation to a single dose in Oct. 2022 due to the ongoing shortage.
Vivekanandan called the vaccine shortage "very concerning."
NEW ANTIBIOTIC KILLS DEADLY, DRUG-RESISTANT BACTERIA IN ‘SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGH’
"This is a serious infection, and we must invest financial and other resources to reduce the worldwide burden," he told Fox News Digital.
"International resources need to be committed, and partnerships with pharmaceutical companies need to happen to help produce more vaccines."
Vivekanandan also urged people who are traveling from the U.S. to other countries to review the CDC’s travel guidance and get any required vaccines.
"I would also recommend that people follow good travel medicine guidance, such as drinking bottled water, eating well-cooked food and making sure to have good hand hygiene," he added.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
"As the WHO has stated, we need to have multi-pronged approaches, with a combination of surveillance, water, sanitation and hygiene, social mobilization, treatment, and oral cholera vaccines available for communities at high risk."
On the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website, Vaxchora is listed as a "resolved shortage."
The FDA noted that Emergent Travel Health, manufacturer of the vaccine, announced in May 2021 the temporary discontinuation and distribution of Vaxchora, "due to a significant reduction of international travel caused by the COVID-19 pandemic."
The shortage is listed as having been resolved in May 2023.
Fox News Digital reached out to WHO, the FDA and Emergent requesting comment.
1 year 2 months ago
Health, outbreaks, Bacteria, viruses, lifestyle, health-care, infectious-disease, World
Health Archives - Barbados Today
Pandemic experts express concern over avian influenza spread to humans
Dr Jeremy Farrar, Chief Scientist at the World Health Organization (WHO), said that the avian influenza virus – which is also known as H5N1 – has had an “extremely high” mortality rate among the several hundred people known to have been infected with it to date.
To date, no human-to-human H5N1 transmission has been recorded.
Dr Jeremy Farrar, Chief Scientist at the World Health Organization (WHO), said that the avian influenza virus – which is also known as H5N1 – has had an “extremely high” mortality rate among the several hundred people known to have been infected with it to date.
To date, no human-to-human H5N1 transmission has been recorded.
“H5N1 is (an) influenza infection, predominantly started in poultry and ducks and has spread effectively over the course of the last one or two years to become a global zoonotic – animal – pandemic,” he said.
“The great concern, of course, is that in doing so and infecting ducks and chickens – but now increasingly mammals – that that virus now evolves and develops the ability to infect humans. And then critically, the ability to go from human-to-human transmission.”
Cattle mystery
Commenting on an ongoing outbreak of H5N1 virus among dairy cows in the United States, the WHO senior official urged further close monitoring and investigation by public health authorities, “because it may evolve into transmitting in different ways”.
He added: “Do the milking structures of cows create aerosols? Is it the environment which they’re living in? Is it the transport system that is spreading this around the country? This is a huge concern and I think we have to … make sure that if H5N1 did come across to humans with human-to-human transmission, that we were in a position to immediately respond with access equitably to vaccines, therapeutics and diagnostics.”
SOURCE: United Nations
The post Pandemic experts express concern over avian influenza spread to humans appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 3 months ago
Health, World
Dominican Embassy in Belgium’s initiative on mental health
Belgium.- As part of the International Women’s Day commemoration activities, the Dominican Embassy in Belgium and Luxembourg organized two special discussions on mental health tailored for the Dominican diaspora in these regions. These sessions were led by renowned Dominican psychiatrist and therapist, Alexandra Híchez.
Belgium.- As part of the International Women’s Day commemoration activities, the Dominican Embassy in Belgium and Luxembourg organized two special discussions on mental health tailored for the Dominican diaspora in these regions. These sessions were led by renowned Dominican psychiatrist and therapist, Alexandra Híchez.
Both events, held over the weekend of March 16-17, at the Beford Hotel in Brussels and the Hotel Royal in Luxembourg, focused on addressing the mental health challenges and concerns faced by the Dominican diaspora. The aim was to raise awareness about the importance of mental well-being for Dominican migrants residing in Brussels and Luxembourg, providing them with a platform to share their experiences and reflections on the topic.
During her presentations, Dr. Híchez provided valuable insights and practical advice to enhance emotional and psychological well-being, especially in the context of migration. She also discussed significant topics such as women’s empowerment and their importance in contemporary society, along with other psychosocial risk factors.
The events commenced with welcoming remarks from Ambassador Iván Ogando Lora, who expressed gratitude to all participants and Dr. Híchez for her enthusiastic commitment to conducting these discussions. Ambassador Ogando Lora emphasized the significance of addressing mental health issues within migrant communities, particularly among women, whose migration and adaptation to a new country often entail significant emotional and psychological challenges.
He underscored that these discussions are part of the ongoing commitment of the mission to support the hardworking Dominican community in Belgium and Luxembourg, particularly in crucial areas like mental health, which contribute to strengthening unity and solidarity.
These activities were made possible with the support of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Dominican Republic (MIREX) and Air Europa. Special acknowledgment is extended to Mrs. Gloria Paniagua, Veridania Mercedes, and Mórela Segura of the Bedford Hotel for their cooperation in facilitating the events.
1 year 4 months ago
Health, World
Health Archives - Barbados Today
Meta investigated over illicit drug sales: report
United States authorities are investigating Meta over its role in the illicit sale of medications, The Wall Street Journal reported Saturday.
Citing documents and people close to the matter, the American business daily said prosecutors in the southern US state of Virginia are looking into whether the company’s social media platforms are facilitating and profiting from the illegal sale of drugs.
Prosecutors have asked for records on “violative drug content on Meta’s platforms and/or the illicit sale of drugs via Meta’s platforms,” according to copies of subpoenas reviewed by The Wall Street Journal.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been helping with the investigation, the paper reported.
“The sale of illicit drugs is against our policies and we work to find and remove this content from our services,” Meta told the Journal in a statement, adding that it “proactively cooperates” with law enforcement to help combat the sale of illicit drugs.
Contacted by AFP on Saturday morning, neither the FDA nor Meta would comment.
On Friday, Nick Clegg, president of global affairs at Meta, said the company had joined an effort alongside the US State Department, the United Nations and Snapchat to help disrupt the sale of synthetic drugs online and educate users about the risks.
“The opioid epidemic is a major public health issue that requires action from all parts of US society,” Clegg wrote on X.
More than 700,000 people died of opioid overdoses between 1999 and 2022, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
SOURCE: AFP
The post Meta investigated over illicit drug sales: report appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 4 months ago
Health, World
COVID-19 Pandemic persists with evolving virus, WHO warns
London.- Maria van Kerkhove, the World Health Organization’s technical lead on COVID-19, cautioned that the world remains in the grip of the COVID-19 pandemic, despite the situation being less severe than in previous years. The ongoing evolution of the virus and continued hospitalizations underscore the persistent health risk.
London.- Maria van Kerkhove, the World Health Organization’s technical lead on COVID-19, cautioned that the world remains in the grip of the COVID-19 pandemic, despite the situation being less severe than in previous years. The ongoing evolution of the virus and continued hospitalizations underscore the persistent health risk.
In a press conference addressing the global rise in COVID-19, influenza, and other respiratory diseases, Van Kerkhove highlighted that while death rates have drastically decreased from peak levels, approximately 10,000 deaths are still occurring monthly based on data from fifty countries. The United States accounted for half of the deaths reported last month, raising concerns about underreporting in various regions.
Wastewater analysis suggests that the actual spread of the coronavirus could be significantly higher than reported figures, potentially 2 to 19 times greater. The recent holiday season saw an increase in communicable respiratory diseases, including COVID-19, flu, RSV viruses, and other seasonal pathogens.
The WHO noted a recent 42% rise in hospitalizations and a 62% increase in ICU admissions due to COVID-19, although these figures are based on incomplete data from only about twenty countries. Van Kerkhove emphasized that while the current situation doesn’t match the peak crisis levels of the pandemic, COVID-19 remains a global health threat and continues to cause avoidable problems.
The issue of “long COVID” was also addressed, with approximately 6% of patients experiencing multi-organ symptoms lasting months or years post-recovery. Van Kerkhove expressed concern about potential long-term heart, lung, or neurological problems emerging in the future.
Acknowledging a sense of complacency four years into the pandemic, Van Kerkhove pointed out the significant mental health impacts of COVID-19 on those directly affected and those who lost loved ones. She reiterated WHO’s recommendations for vaccinations, including booster doses for older individuals, health workers, and vulnerable groups every six to twelve months.
Additionally, the use of masks is advised in healthcare settings and by sick individuals to reduce the spread of respiratory diseases.
1 year 6 months ago
Health, World
Health Archives - Barbados Today
A new cure for sickle cell disease may be coming. Health advisers will review it next week
SOURCE: AP – The only cure for painful sickle cell disease today is a bone marrow transplant. But soon there may be a new cure that attacks the disorder at its genetic source.
On Tuesday, advisers to the Food and Drug Administration will review a gene therapy for the inherited blood disorder, which in the U.S. mostly affects Black people. Issues they will consider include whether more research is needed into possible unintended consequences of the treatment.
If approved by the FDA, it would be the first gene therapy on the U.S. market based on CRISPR, the gene editing tool that won its inventors the Nobel Prize in 2020.
The agency is expected to decide on the treatment in early December, before taking up a different sickle cell gene therapy later that month.
Dr. Allison King, who cares for children and young adults with sickle cell disease, said she’s enthusiastic about the possibility of new treatments.
“Anything that can help relieve somebody with this condition of the pain and the multiple health complications is amazing,” said King, a professor at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. “It’s horribly painful. Some people will say it’s like being stabbed all over.”
The disorder affects hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. A genetic mutation causes the cells to become crescent-shaped, which can block blood flow and cause excruciating pain, organ damage, stroke and other problems.
Millions of people around the world, including about 100,000 in the U.S., have the disease. It occurs more often among people from places where malaria is or was common, like Africa and India, and is also more common in certain ethnic groups, such as people of African, Middle Eastern and Indian descent. Scientists believe being a carrier of the sickle cell trait helps protect against severe malaria.
Current treatments include medications and blood transfusions. The only permanent solution is a bone marrow transplant, which must come from a closely matched donor without the disease and brings a risk of rejection.
No donor is required for the one-time gene therapy, “exa-cel,” made by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics. This new treatment involves permanently changing DNA in a patient’s blood cells.
The goal is to help the body go back to producing a fetal form of hemoglobin — which is naturally present at birth but then switches to an adult form that’s defective in people with sickle cell disease.
When patients undergo the treatment, stem cells are removed from their blood and CRISPR is used to knock out the switching gene. Patients get medicines to kill off other flawed blood-producing cells and then are given back their own altered stem cells.
The treatment has been tested in a relatively small number of patients thus far, the nonprofit Institute for Clinical and Economic Review said in an evidence report.
In a briefing document released Friday before the advisory committee meeting, Vertex said 46 people got the treatment in the pivotal study. Of 30 who had at least 18 months of follow-up, 29 were free of pain crises for at least a year and all 30 avoided being hospitalized for pain crises for that long.
The company called the treatment “transformative” and said it has “a strong safety profile.”
Victoria Gray, of Mississippi, the first patient to test the treatment, shared her experience with researchers at a scientific conference earlier this year. She described suffering with terrible bouts of pain since childhood and receiving high-dose pain medications and sometimes blood transfusions. She described feeling she “was being reborn” the day she got the gene therapy.
Now, she’s able to run around with her kids and work a full-time job. “My children no longer have a fear of losing their mom to sickle cell disease,” she said.
But the FDA is asking an outside panel of gene therapy experts next week to discuss a lingering issue that often comes up when discussing CRISPR: the possibility of “off-target effects,” which are unexpected, unwanted changes to a person’s genome. The FDA is looking for advice on whether the company’s research on such effects was adequate to assess the risk or whether additional studies are needed. While the agency doesn’t have to follow the group’s advice, it often does.
If the treatment is allowed on the market, the company has proposed a post-approval safety study, product labeling outlining potential risks and continuing research.
The FDA is expected to decide on the second gene therapy for sickle cell, made by Bluebird Bio, before the end of the year. Bluebird’s treatment works differently. It aims to add functional copies of a modified gene, which helps red blood cells produce “anti-sickling” hemoglobin that prevents or reverses misshapen cells.
The companies have not released potential prices for either therapy, but the institute report said prices up to around $2 million would be cost-effective. By comparison, research earlier this year showed medical expenses for current sickle cell treatments, from birth to age 65, add up to about $1.6 million for women and $1.7 million for men.
King, the St. Louis doctor, acknowledged the new treatments would be expensive. “But if you think about it,” she said, “how much is it worth for someone to feel better and not be in pain and not be in the hospital all the time?”
The post A new cure for sickle cell disease may be coming. Health advisers will review it next week appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 9 months ago
A Slider, Health, World
Jamaica declares Dengue fever outbreak with hundreds of confirmed and suspected cases
Health officials in Jamaica have declared an outbreak of the dengue fever Saturday with at least 565 suspected, presumed and confirmed cases in the Caribbean nation.
Health officials in Jamaica have declared an outbreak of the dengue fever Saturday with at least 565 suspected, presumed and confirmed cases in the Caribbean nation.
Jamaica’s Ministry of Health and Wellness says the outbreak comes as its National Surveillance Unit "advised that Jamaica has surpassed the dengue epidemic threshold for July and August and is on a trajectory to do the same for the month of September."
"The dominant strain is Dengue Type 2, which last predominated in 2010," it said. "There are no dengue-related deaths classified at this time, however, six deaths are being investigated."
Health officials say there currently are at least 78 confirmed cases of the mosquito-borne disease in Jamaica.
MOSQUITOS, FEARED FOR SPREADING DENGUE, NOW BEING BRED TO FIGHT THE DISEASE
"Meanwhile, approximately 500 temporary vector control workers have been engaged and deployed across the island to high-risk communities along with 213 permanent workers," the Ministry of Health and Wellness also said.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says dengue viruses are "spread to people through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito."
About one in four people infected will get sick, with mild symptoms including nausea, vomiting, rash, aches and pains, according to the CDC.
Recovery takes about a week.
DENGUE FEVER CASES COULD REACH NEAR-RECORD HIGHS THIS YEAR
Around 1 in 20 people infected will develop severe dengue, which the CDC says "can result in shock, internal bleeding, and even death."
"The Ministry and Regional Health Authorities have made the necessary preparations for a possible outbreak," said Christopher Tufton, the Minister of Health in Jamaica.
The Ministry is warning the public in Jamaica that the Aedes aegypti mosquito "breeds in any containerized environment" that can hold water, such as drums, tires, buckets and animal feeding containers.
"Persons are urged to play their part in ensuring that the cases are minimized by monitoring water storage containers for mosquito breeding, keeping surroundings free of debris, destroying or treating potential mosquito breeding sites, wearing protective clothing, using mosquito repellent and, as much as possible, staying indoors at dusk with windows and doors closed," it also said.
1 year 10 months ago
infectious-disease, World, caribbean-region, Health
Health Archives - Barbados Today
Local lab could become WHO centre to detect antimicrobial resistance
The Best-dos Santos Public Health Laboratory could soon become a World Health Organisation (WHO) collaborating centre for Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) detection and surveillance.
This was revealed by PAHO/WHO Representative for Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean Countries (ECC) Dr Amalia Del Riego during the opening ceremony of a training workshop for laboratory technologists who work in public health laboratories in Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Haiti, St Vincent and the Grenadines and Suriname.
The workshop is taking place at the Best-dos Santos Public Health Laboratory from September 19 to 22.
Entitled Training on Molecular Detection and Diagnosis of Carbapenemase Genes in Gram-Negative Bacteria, the training forms phase two of the Cooperation among Countries for Health Development (CCHD) project on AMR detection and surveillance.
WHO collaborating centres assist WHO support countries to build capacity to develop and implement AMR surveillance.
Dr Del Riego said of the training: “This and many other multi-country trainings that have happened just this year in the Best-dos Santos Laboratory demonstrate the interest this laboratory and the Government of Barbados have in fostering south-to-south collaboration. We hope this soon translates into Best-dos Santos becoming a WHO collaborating centre on AMR.
“We appreciate the support provided by the Government of Argentina in the past, and currently for antimicrobial resistance detection and surveillance across the Caribbean. We wish to acknowledge the support of Malbran Institute (Buenos Aires, Argentina), a WHO collaborating centre for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance,” she added.
Molecular training provides countries with the capacity to diagnose AMR, one of the most important emerging threats. The training involves the detection of disease-causing organisms which are virtually resistant to all known antibiotics.
Chief Medical Officer Dr Kenneth George reiterated that AMR training is a priority for Barbados, noting that AMR diseases are becoming more prevalent.
He therefore thanked the Government of Argentina for continuing support for training.
“Your support, both technically and financially, through the Malbran Institute is designed to support and promote antimicrobial stewardship across the Caribbean,” Dr George said.
The CMO recalled that in 2019, the World Health Assembly unanimously adopted a resolution calling for continued high-level commitments to implement multisectoral national action plans.
“Barbados is in the process of developing a framework to achieve this goal,” he said.
Dr George also expressed his appreciation to PAHO for providing its technical expertise to the Best-dos Santos Public Health Laboratory.
PAHO was credited with providing influenza surveillance and laboratory testing support, “with a view to establishing the Best-dos Santos Laboratory as a recognised influenza testing site in the subregion”.
Chargé d’Affaires of the Embassy of the Argentine Republic in Barbados, Vanesa Romani, recounted that in 2018 Argentina, PAHO and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) signed a commitment establishing the Cooperation among Countries for Health Development (CCHD) project. This made it possible for two technicians from the Best-dos Santos Laboratory to attend training in Argentina.
Romini said the training received has improved the ability to deal with emergencies. (PR)
The post Local lab could become WHO centre to detect antimicrobial resistance appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 10 months ago
A Slider, Education, Health, Health Care, Technology, World
Health Archives - Barbados Today
Elderly Chinese keep fit, socialise in specially-provided spaces
At any given time during daylight hours, elderly Chinese gather in large groups to exercise and socialise.
At any given time during daylight hours, elderly Chinese gather in large groups to exercise and socialise.
It was one of my thought-provoking discoveries during my visit last month to the East Asian nation where life expectancy is 77.47 years.
At almost every place of interest, delegates of the Seminar for National Press Officers and Journalists from Belt and Road Countries, who were in Beijing from July 12 to July 25, witnessed scores of senior citizens working up a sweat.
No matter their physical structure or gender, many of them engaged in a variety of exercise routines – some simple, others testing their mental and physical strength. Others engaged in dance sessions, sang or played musical instruments.
The game Ti Zian Ji, during which players use their feet instead of racquets to hit a shuttlecock, appeared to be a favourite. According to unofficial reports, some Chinese would spend hours playing the game.
But whatever they were doing, these seniors all looked stress-free and relaxed.
It was explained to the 14 delegates that China’s elderly care policy plans request local governments to set up facilities for senior education and leisure, including parks, green spaces, and sporting facilities.
Some of us remarked that we would love to see similar spaces being created for elderly citizens in our own countries.
It made me think that even though the elderly in Barbados flock to the beaches for water therapy and exercise, local authorities could perhaps follow China’s lead and develop additional safe recreational spaces across the island for older folk.
While on a visit to the Temple of Heaven, some of us joined in a dancing session in the recreational area there.
The Temple of Heaven is the place where the emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasties “worshipped the heaven” and “prayed for the good harvest”.
Tour guide Lili Yang said that almost every day, retirees visit the location, which is also used as a public park, to exercise.
“We have a lot of public parks in Beijing provided by the local government and they are open to retired people to go for morning and evening exercise. We have a lot of retired people, so going to the parks is a kind of social life for Chinese local elderly people,” Yang said.
“They dance and they play musical instruments and they do all kinds of activities that help them to entertain themselves. Whether they are dancing, singing or exercising, you can see on their faces that they are very happy with what they are doing. The retired people are very happy that they have these parks where they can go.”
Another highlight of the two-week seminar was the visit to the Yunnan Ethnic Village, located on the south side of Kunming.
The village is one of the most popular tourist attractions in the Yunnan province’s capital and largest.
Ethnic minority villages, including those of the Dai, Bai and Yi people, have their own folk customs and craft performances.
During minority festivals such as the Songkran Festival in April and the Torch Festival in July and August, the ethnic village also hosts lively celebrations which thousands travel from far and near to see.
Tomorrow, we bring the final installment of Anesta Meets China, a five-part series about the experience of Barbados TODAY journalist Anesta Henry in China.
The post Elderly Chinese keep fit, socialise in specially-provided spaces appeared first on Barbados Today.
1 year 11 months ago
asia, Health, Local News, Rejuvenate, Travel, World